Automated CI/CD for Monorepo's
Monorepo is an approach in managing source code under a product, team or company within a single repo as oppose to multi-repo where a single product/application is contained within its own git repository.
The two approaches has its own pro’s and con’s. In this article i will not be discussing on what is the best approach as it entirely matters on the context we work, rather i will walk the through the challenges of Automated CI/CD with mono-repo and how we can over come them with structure and some magic with Jenkins Pipeline.
Challenges
Due to the nature of multiple applications residing in a single repo it is not trivial to setup a CI/CD job that detects changes and executes only the impacted applications related CI/CD job. Some of the steps that contain in a typical pipeline are,
- Building the code
- Running automated tests
- Creating and versioning a deployable artifact
- Deploying that artifact
Lets look at how we can tackle this problem with Jenkins.
Some Jenkins Magic
sample structure in a mono-repo setup with jenkins pipeline
.
├── src
├── react-app
├── Jenkinsfile
├── node-app
├── Jenkinsfile
└── Jenkinsfile # main jenkinsfile
If we consider a structure like above, with jenkins we could setup the main Jenkinsfile in the root of the repository as a multi-branch jenkins job. This job can be connected with your remote repository such that it triggers via a webhook when a PR is merged to your mainline branch. You can get creative with the triggers depending on the workflow your team follows.
A stage inside the main Jenkinsfile is shown below
stage('Execute Jobs') {
failFast false
parallel {
stage('react-app ci') {
when {
changeset "src/react-app/**"
}
steps {
build job: "react-app-job", parameters: [string(name: 'branch_name', value: env.BRANCH_NAME)]
}
}
stage('node-app ci') {
when {
changeset "src/node-app/**"
}
steps {
build job: "node-app-job", parameters: [string(name: 'branch_name', value: env.BRANCH_NAME)]
}
}
}
}
In the above example the changeset condition walks through the git changelog for that particular change and checks if there is any change within the given path. If a change is detected then the build job step executes the related jenkins job.
Note - failFast is set to false to avoid failure of the entire pipeline if one job fails.
Once we have this setup we can go about and setup separate pipeline jobs for each application in the repository.
Below is an example on how the main multi-branch job will look in Jenkins
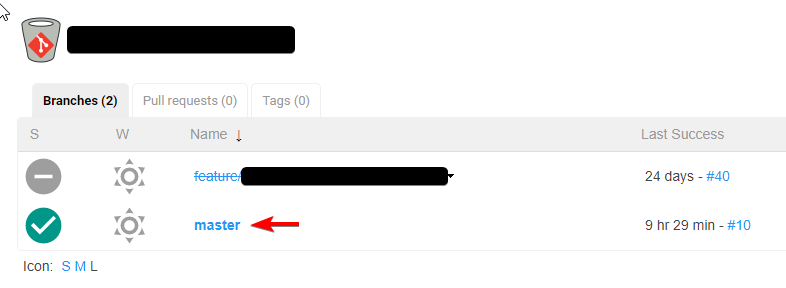 In the above image the multi-branch job has executed when a change has been pushed to the master branch. When we navigate into the master branch execution we can see the pipeline as shown below,
In the above image the multi-branch job has executed when a change has been pushed to the master branch. When we navigate into the master branch execution we can see the pipeline as shown below,
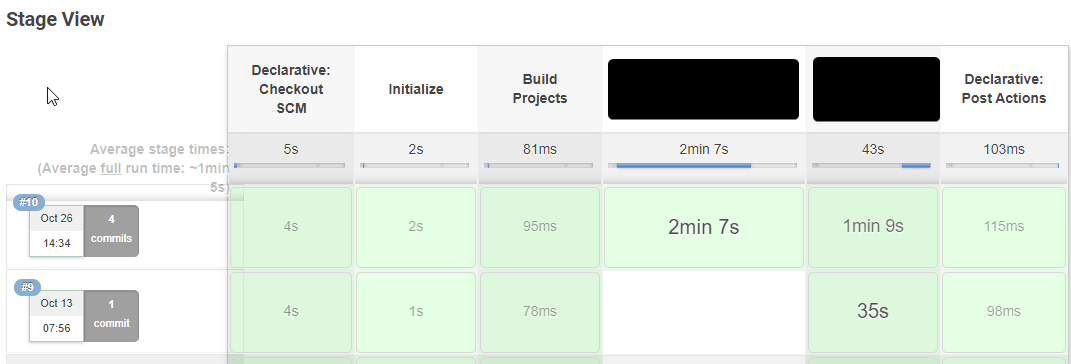
In the stage view we can see that build #9 contains changes only for 1 application and build #10 contains changes for both.
This is an awesome and quick setup with Jenkins for a monorepo. I’m a big fan of Jenkins due to its flexibility and extensibility specially with declarative Jenkins Pipeline.